VO2 max is a crucial measurement for anyone looking to improve their cardiovascular health, endurance, or overall fitness. Whether you’re a competitive athlete or someone just getting started on a fitness journey, understanding and improving VO2 max can make a substantial difference in your performance and well-being. This guide delves into what VO2 max is, why it matters, and how you can measure and improve it to achieve better health outcomes, from athletic performance to longevity.
In This Article
What is VO2 Max?
VO2 max stands for “Volume of Oxygen Maximal,” which refers to the maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilize during intense physical activity. It is considered the best indicator of cardiorespiratory fitness, highlighting the efficiency with which your cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together to deliver oxygen to your muscles during exercise.
Essentially, VO2 max reflects how much oxygen your muscles can use to produce energy at peak effort. The higher your VO2 max, the more oxygen your body can process and transport to your working muscles, allowing for better endurance and higher exercise performance.
While VO2 max is often associated with elite athletes, it’s not just a metric for performance. It’s also a valuable indicator of overall health and longevity. Improving VO2 max can benefit not only athletes but anyone looking to enhance their cardiovascular health and quality of life.
Why VO2 Max Matters: More Than Just Athletic Performance
VO2 max is a key marker of overall health, and its benefits extend far beyond just performance in endurance sports. Here’s why VO2 max matters:
- Cardiovascular Health: A higher VO2 max is closely linked to a healthier heart. Since VO2 max represents the efficiency of oxygen delivery and utilization, it reflects how well your heart, lungs, and muscles are working together. This is vital for reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases like heart attacks, stroke, and hypertension. Studies show that individuals with higher VO2 max levels tend to have better heart health and lower levels of arterial stiffness, which is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
- Longer Lifespan: VO2 max has been shown to correlate with longer life expectancy. Research indicates that people with a higher VO2 max live longer, healthier lives because they have reduced risks of chronic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases. In fact, it has been found to be a more reliable predictor of life expectancy than other traditional health markers like cholesterol levels or blood pressure. Regular physical activity that boosts VO2 max helps slow down the aging process, allowing people to enjoy a longer, more active life.
- Improved Mental Health: Regular exercise that increases VO2 max also has positive effects on mental health. Studies show that aerobic exercises, like running or cycling, which improve VO2 max, are effective at reducing symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. Additionally, physical activity improves cognitive function and memory, especially in older adults. Therefore, improving VO2 max can not only boost your physical health but also enhance your mood and mental well-being.
- Better Performance and Endurance: For athletes, VO2 max is critical to performance. It indicates how well the body can sustain prolonged exercise at high intensities. A higher VO2 max allows athletes to push harder, recover faster, and perform better in endurance sports, such as running, cycling, swimming, and rowing. Whether you’re training for a marathon or just enjoy a long jog, increasing your VO2 max will help you go further with less fatigue.
VO2 Max Norms by Age and Gender
Understanding where your VO2 max falls relative to others is helpful when setting goals and tracking progress. Below are general benchmarks for VO2 max based on age and gender, established by the American College of Sports Medicine. These norms help identify whether your VO2 max is within the average range for your age group and how you compare to others in terms of cardiovascular fitness.
For Men:
| Age Range | Poor | Fair | Average | Good | Excellent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤29 years | ≤24.9 | 25-33.9 | 34-43.9 | 44-52.9 | ≥53 |
| 30-39 years | ≤22.9 | 23-30.9 | 31-41.9 | 42-49.9 | ≥50 |
| 40-49 years | ≤19.9 | 20-26.9 | 27-38.9 | 39-44.9 | ≥45 |
| 50-59 years | ≤17.9 | 18-24.9 | 25-37.9 | 36-42.9 | ≥43 |
| 60-69 years | ≤15.9 | 16-22.9 | 23-35.9 | 36-40.9 | ≥41 |
For Women:
| Age Range | Poor | Fair | Average | Good | Excellent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤29 years | ≤23.9 | 24-30.9 | 31-38.9 | 39-48.9 | ≥49 |
| 30-39 years | ≤19.9 | 20-27.9 | 28-36.9 | 37-44.9 | ≥45 |
| 40-49 years | ≤16.9 | 17-24.9 | 25-34.9 | 35-41.9 | ≥42 |
| 50-59 years | ≤14.9 | 15-21.9 | 22-33.9 | 34-39.9 | ≥40 |
| 60-69 years | ≤12.9 | 13-20.9 | 21-32.9 | 33-36.9 | ≥37 |
These benchmarks provide a general guide for assessing your cardiovascular fitness. However, remember that individual variations exist, and VO2 max is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to evaluating health and fitness.
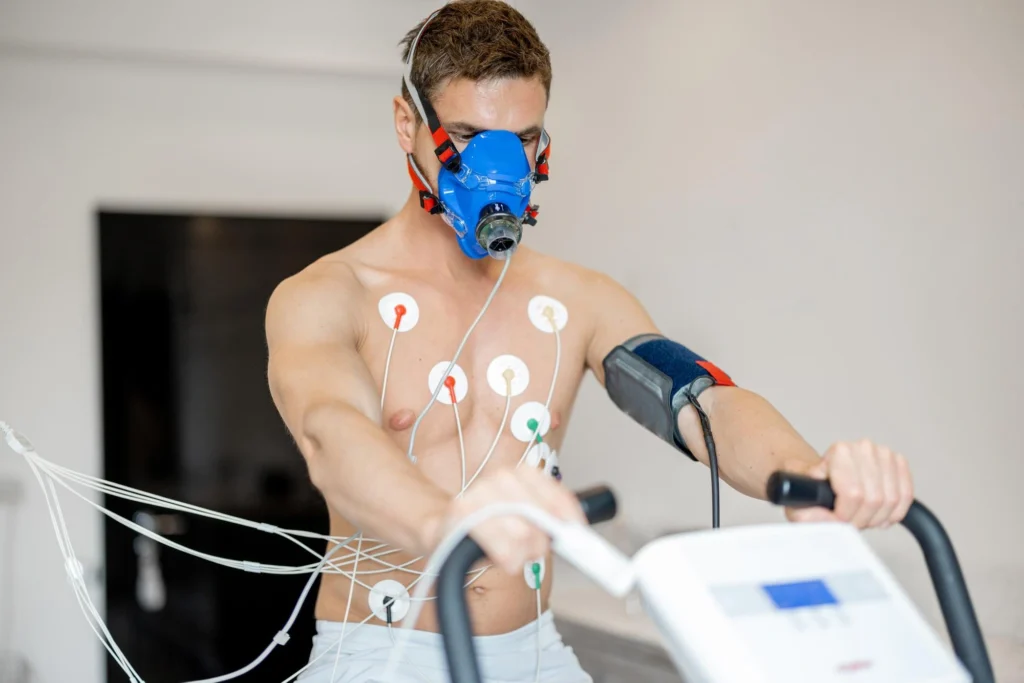
How is VO2 Max Measured?
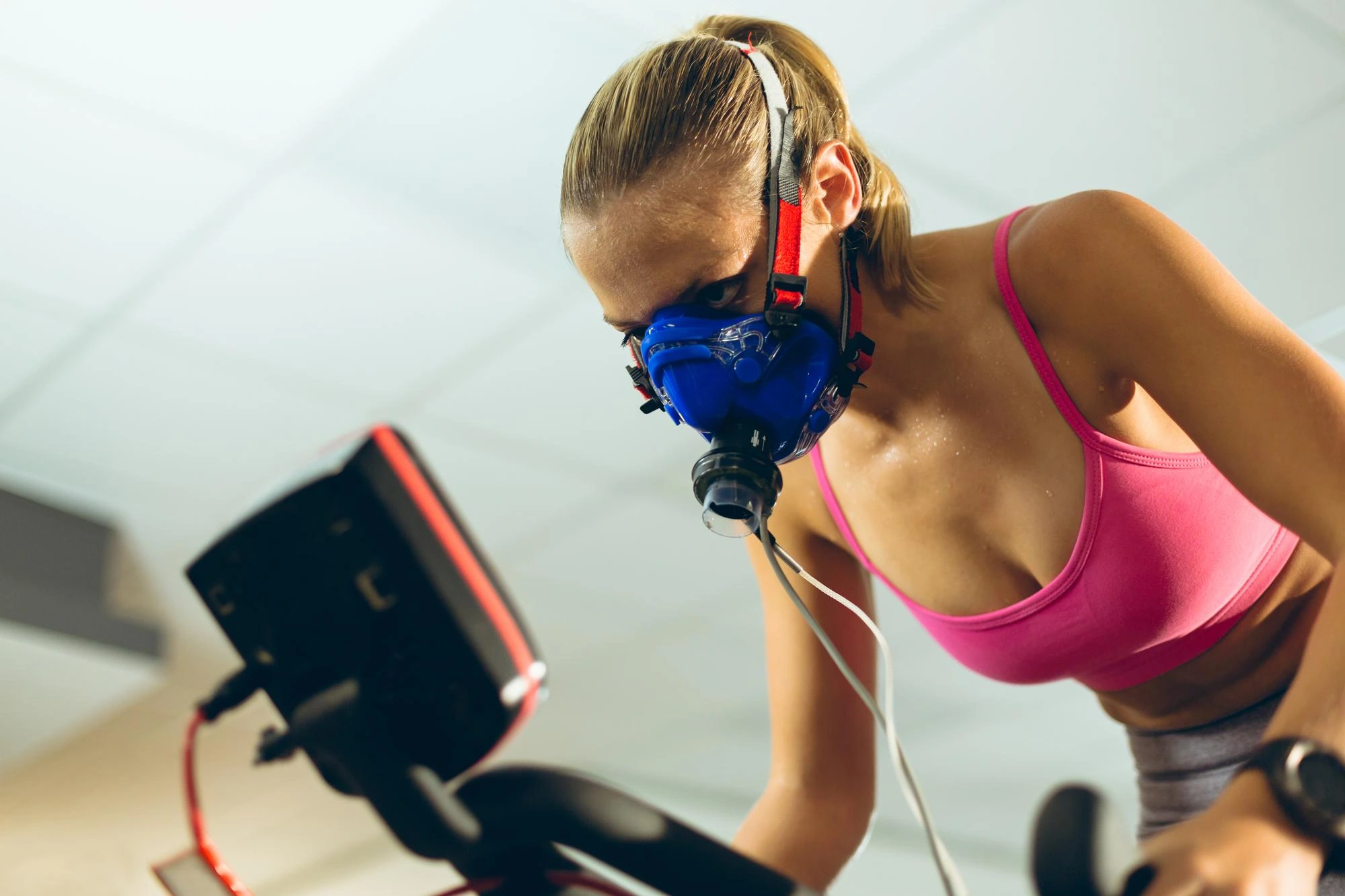
The most accurate way to measure VO2 max is through a Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test (CPET). This test involves exercising on a treadmill or cycle ergometer while wearing a mask that measures the amount of oxygen you consume. As the intensity of the exercise increases, the machine records how much oxygen you use, and VO2 max is determined at the point where your oxygen consumption plateaus, despite increasing exercise intensity.
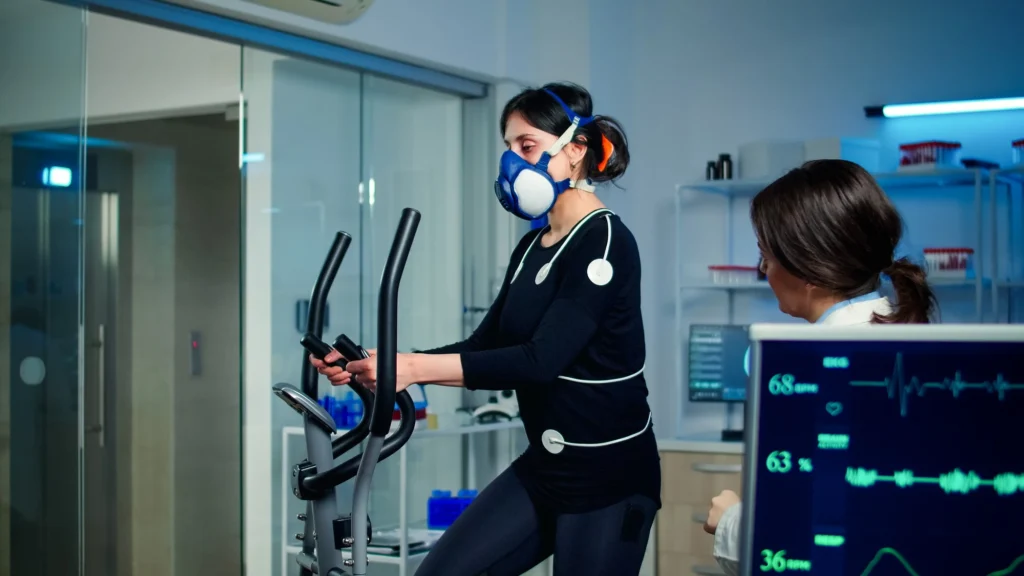

While this method provides the most precise measurement, it may not be accessible to everyone due to cost or availability. Fortunately, many wearable fitness trackers and smartwatches (such as those from Garmin, Apple, and Fitbit) offer VO2 max estimates based on your heart rate and activity level. While these devices aren’t as accurate as CPET, they are still valuable tools for tracking trends in VO2 max over time.
Factors That Affect VO2 Max
Several factors influence your VO2 max, including:
- Genetics: Genetics play a significant role in determining your baseline VO2 max. Some people are naturally more predisposed to having a higher VO2 max due to their genetic makeup.
- Age: VO2 max generally declines with age, primarily due to decreases in cardiovascular and respiratory efficiency. However, this decline can be slowed with regular exercise.
- Sex: On average, men tend to have a higher VO2 max than women, mainly due to differences in muscle mass and hemoglobin levels, which affect oxygen transport.
- Fitness Level: Regular aerobic exercise can significantly improve VO2 max by enhancing heart efficiency, lung capacity, and muscle oxygen utilization. The more conditioned your cardiovascular system is, the higher your VO2 max will be.
- Altitude: People living at higher altitudes often have a higher VO2 max compared to those living at sea level. This is because the body adapts to lower oxygen levels by producing more red blood cells, improving oxygen delivery to tissues.
How to Improve Your VO2 Max
Improving VO2 max requires a combination of consistent aerobic exercise, targeted training strategies, and sometimes lifestyle changes. Here are some of the most effective methods to enhance VO2 max:
- Aerobic Exercise: Engaging in consistent, moderate-intensity aerobic exercise is one of the best ways to improve VO2 max. Activities like walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling help increase your body’s ability to utilize oxygen, enhancing endurance and cardiovascular efficiency.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT is an effective method for rapidly boosting VO2 max. It involves alternating between short bursts of intense activity and recovery periods. HIIT can significantly improve cardiovascular health, burn fat, and increase VO2 max in a shorter amount of time compared to steady-state aerobic exercise.
- Strength Training: While strength training is not traditionally associated with VO2 max, circuit-based resistance training (involving minimal rest between exercises) can help improve cardiovascular endurance while also building muscle mass. This type of training can complement aerobic activities and contribute to an increase in VO2 max.
- Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition supports the body’s ability to improve VO2 max. Maintaining optimal iron levels, for example, is critical, as iron is necessary for oxygen transport in the blood. Iron-rich foods like leafy greens, lean meats, and legumes can improve oxygen delivery and support endurance training.
- Consistency and Progression: To see significant improvements in VO2 max, consistency is key. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your exercise routines to progressively challenge your cardiovascular system. Over time, this progressive overload will lead to improved VO2 max and overall endurance.
Health Benefits of Improving VO2 Max
Improving your VO2 max has numerous health benefits, including:
- Enhanced Cardiovascular Health: Higher VO2 max levels are associated with lower risks of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. Regular aerobic exercise that improves VO2 max can reduce arterial stiffness and improve blood vessel function, both key indicators of heart health.
- Improved Blood Sugar and Lipid Profiles: Exercise that boosts VO2 max also helps regulate blood sugar levels, improving insulin sensitivity and reducing the risk of diabetes. Additionally, aerobic training can help improve cholesterol levels, lowering LDL (“bad” cholesterol) and increasing HDL (“good” cholesterol).
- Increased Lifespan: Studies have shown that individuals with higher VO2 max levels tend to live longer, healthier lives. Regular aerobic exercise that boosts VO2 max has been linked to a reduction in all-cause mortality and a decreased risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes and obesity.
- Better Mental Health: Cardiovascular exercise that improves VO2 max is linked to improved mental health. Aerobic activity has been shown to reduce stress, anxiety, and depression, while also improving cognitive function and memory. This makes improving VO2 max beneficial for mental well-being, especially as we age.
Conclusion
VO2 max is a critical indicator of cardiovascular health and aerobic fitness. Whether you’re an athlete looking to optimize performance or someone looking to improve overall health, enhancing VO2 max through regular aerobic exercise, HIIT, strength training, and proper nutrition can have profound benefits. By understanding VO2 max and taking steps to improve it, you can enhance your endurance, increase your lifespan, and enjoy better mental and physical health.
References
- American Heart Association. (2016). Scientific Statement: Exercise and Cardiovascular Health. Circulation.
- American College of Sports Medicine. (2014). ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription (11th ed.).
- Buchheit, M., & Laursen, P. B. (2013). Testing for Athlete Monitoring: Motivation, Posture, and Performance. Journal of Sports Sciences.








0 Comments